Biological relevance
Furanocoumarins are produced by plants as a defense mechanism against predation. Some are toxic, while others cause intense skin reactions. Some can cause altered dosing of drugs in humans.
These compounds are synthesized from phenylalanine, and much is known about the synethic pathways (From Berenbaum Lab at Illinois): 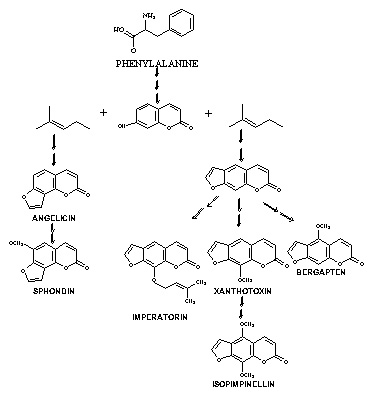
Photoactivity and DNA Binding
Several members of this class of compounds are fairly efficient absorbers of ultraviolet light, and have the ability to bind to DNA. When exposed to UV radiation, furanocoumarins cross-link pyrimidine bases on opposing DNA strands. This blocks normal function like replication and transcription.